Page 44 - Bus101FlipBook
P. 44
2-10 Economics — A Primer [CH 2
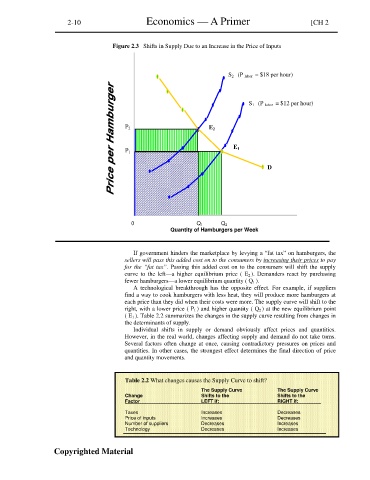
Figure 2.3 Shifts in Supply Due to an Increase in the Price of Inputs
S 2 (P labor = $18 per hour)
S 1 (P labor = $12 per hour)
P 2 E 2
E 1
P 1
D
0 Q 1 Q 2
Quantity of Hamburgers per Week
If government hinders the marketplace by levying a “fat tax” on hamburgers, the
sellers will pass this added cost on to the consumers by increasing their prices to pay
for the “fat tax”. Passing this added cost on to the consumers will shift the supply
curve to the left—a higher equilibrium price ( E 2 ). Demanders react by purchasing
fewer hamburgers—a lower equilibrium quantity ( Q 1 ).
A technological breakthrough has the opposite effect. For example, if suppliers
find a way to cook hamburgers with less heat, they will produce more hamburgers at
each price than they did when their costs were more. The supply curve will shift to the
right, with a lower price ( P 1 ) and higher quantity ( Q 2 ) at the new equilibrium point
( E 1 ). Table 2.2 summarizes the changes in the supply curve resulting from changes in
the determinants of supply.
Individual shifts in supply or demand obviously affect prices and quantities.
However, in the real world, changes affecting supply and demand do not take turns.
Several factors often change at once, causing contradictory pressures on prices and
quantities. In other cases, the strongest effect determines the final direction of price
and quantity movements.
Table 2.2 What changes causes the Supply Curve to shift?
The Supply Curve The Supply Curve
Change Shifts to the Shifts to the
Factor LEFT if: RIGHT if:
Taxes Increases Decreases
Price of inputs Increases Decreases
Number of suppliers Decreases Increases
Technology Decreases Increases
Copyrighted Material