Page 74 - Calculating Agriculture Cover 20191124 STUDENT - A
P. 74
5-12 Measurements CH 5]
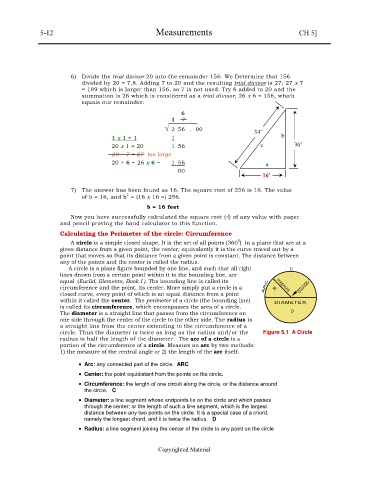
6) Divide the trial divisor 20 into the remainder 156. We Determine that 156
divided by 20 = 7.8. Adding 7 to 20 and the resulting trial divisor is 27; 27 x 7
= 189 which is larger than 156, so 7 is not used. Try 6 added to 20 and the
summation is 26 which is considered as a trial divisor; 26 x 6 = 156, which
equals our remainder.
6
1 7 .
√ 2 56 . 00
34’
1 x 1 = 1 1 b
20 x 1 = 20 1 56 c 30’
20 + 7 = 27 too large
20 + 6 = 26 x 6 = 1 56 a
00
16’
7) The answer has been found as 16. The square root of 256 is 16. The value
2
of b = 16, and b = (16 x 16 =) 256.
b = 16 feet
Now you have successfully calculated the square root (√) of any value with paper
and pencil proving the hand calculator to this function.
Calculating the Perimeter of the circle: Circumference
0
A circle is a simple closed shape. It is the set of all points (360 ) in a plane that are at a
given distance from a given point, the center; equivalently it is the curve traced out by a
point that moves so that its distance from a given point is constant. The distance between
any of the points and the center is called the radius.
A circle is a plane figure bounded by one line, and such that all right C
lines drawn from a certain point within it to the bounding line, are
equal (Euclid, Elements, Book I ). The bounding line is called its
circumference and the point, its center. More simply put a circle is a ARC R RADIUS Center
closed curve, every point of which is an equal distance from a point
within it called the center. The perimeter of a circle (the bounding line) DIAMET ER
is called its circumference, which encompasses the area of a circle.
The diameter is a straight line that passes from the circumference on D
one side through the center of the circle to the other side. The radius is
a straight line from the center extending to the circumference of a
circle. Thus the diameter is twice as long as the radius and/or the Figure 5.1 A Circle
radius is half the length of the diameter. The arc of a circle is a
portion of the circumference of a circle. Measure an arc by two methods:
1) the measure of the central angle or 2) the length of the arc itself.
Arc: any connected part of the circle. ARC
Center: the point equidistant from the points on the circle.
Circumference: the length of one circuit along the circle, or the distance around
the circle. C
Diameter: a line segment whose endpoints lie on the circle and which passes
through the center; or the length of such a line segment, which is the largest
distance between any two points on the circle. It is a special case of a chord,
namely the longest chord, and it is twice the radius. D
Radius: a line segment joining the center of the circle to any point on the circle
Copyrighted Material