Page 167 - Calculating Agriculture Cover 20191124 STUDENT - A
P. 167
CH 14] Calculating Agriculture 14-27
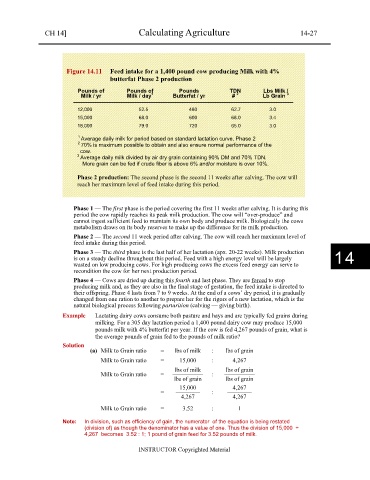
Figure 14.11 Feed intake for a 1,400 pound cow producing Milk with 4%
butterfat Phase 2 production
Pounds of Pounds of Pounds TDN Lbs Milk /
1
3
Milk / yr Milk / day Butterfat / yr # 2 Lb Grain
12,000 52.5 480 62.7 3.0
15,000 68.0 600 68.0 3.4
18,000 79.0 720 65.0 3.0
1 Average daily milk for period based on standard lactation curve. Phase 2
2 70% is maximum possible to obtain and also ensure normal performance of the
cow.
3 Average daily milk divided by air dry grain containing 90% DM and 70% TDN.
More grain can be fed if crude fiber is above 6% and/or moisture is over 10%.
Phase 2 production: The second phase is the second 11 weeks after calving. The cow will
reach her maximum level of feed intake during this period.
Phase 1 — The first phase is the period covering the first 11 weeks after calving. It is during this
period the cow rapidly reaches its peak milk production. The cow will “over-produce” and
cannot ingest sufficient feed to maintain its own body and produce milk. Biologically the cows
metabolism draws on its body reserves to make up the difference for its milk production.
Phase 2 — The second 11 week period after calving. The cow will reach her maximum level of
feed intake during this period.
Phase 3 — The third phase is the last half of her lactation (apx. 20-22 weeks). Milk production
is on a steady decline throughout this period. Feed with a high energy level will be largely 14
wasted on low producing cows. For high producing cows the excess feed energy can serve to
recondition the cow for her next production period.
Phase 4 — Cows are dried up during this fourth and last phase. They are forced to stop
producing milk and, as they are also in the final stage of gestation, the feed intake is directed to
their offspring. Phase 4 lasts from 7 to 9 weeks. At the end of a cows’ dry period, it is gradually
changed from one ration to another to prepare her for the rigors of a new lactation, which is the
natural biological process following parturition (calving — giving birth).
Example Lactating dairy cows consume both pasture and hays and are typically fed grains during
milking. For a 305 day lactation period a 1,400 pound dairy cow may produce 15,000
pounds milk with 4% butterfat per year. If the cow is fed 4,267 pounds of grain, what is
the average pounds of grain fed to the pounds of milk ratio?
Solution
(a) Milk to Grain ratio = lbs of milk : lbs of grain
Milk to Grain ratio = 15,000 : 4,267
lbs of milk lbs of grain
Milk to Grain ratio = ————— : —————
lbs of grain lbs of grain
15,000 4,267
= ———— : ————
4,267 4,267
Milk to Grain ratio = 3.52 : 1
Note: In division, such as efficiency of gain, the numerator of the equation is being restated
(division of) as though the denominator has a value of one. Thus the division of 15,000 ÷
4,267 becomes 3.52 : 1; 1 pound of grain feed for 3.52 pounds of milk.
INSTRUCTOR Copyrighted Material