Page 152 - Calculating Agriculture Cover 20191124 STUDENT - A
P. 152
14-2 Feeds and Feeding CH 14]
Swine, horses and mules, are monogastric animals. As the word monogastric suggests, this type
of digestive system consists of one (“mono”) stomach chamber (“gastric”). The process of digestion
begins with the mouth and the intake of food.
Monogastric: Poultry have a boney beak and no teeth, therefore they do not chew (masticate) their food.
Single-chambered Poultry feed passes into the birds crop. A chicken's crop has a specific function which is to sort food
Stomach. out like a holding tank. When the food is ready and sorted out in the crop, it passes into one of the two
gastric chambers that a chicken has, which are the proventriculus or the gizzard. The “easy” to digest
Proventriculus: A food goes to the proventriculus where it's broken down by hydrochloric acid as well as digestive
standard part of enzymes. Food that is harder to digest and which needs to be “mechanically” broken down passes to
avian anatomy, the gizzard to be processed - this is where muscular contractions combined with some small stones
and is a rod (grit) are needed to process food that is ingested.
shaped organ,
located between As there are thousands of feedstuffs used to formulate animal rations, a discussion of feedstuffs
the esophagus and could be made on the basis of groups or type of feedstuffs by their common characteristics. The
the gizzard of most National Research Council (NRC) in 1972 established such groups. It is important to realize that the
birds. It is generally classification of feedstuffs into categories is imprecise because most feedstuffs are complex multiple
a glandular part of
the stomach that nutrient sources. For example, the same feedstuff may legitimately be considered either an energy
may store and/or feed or a protein supplement, or even a forage, such as Alfalfa, which is a roughage, with a 15.3%
commence protein content, a 1.9% fat content and a 28.6% fiber content. Upon being digested, the energy used to
digestion of food produce cell development, maintenance, and growth come predominantly from the protein as
before it
progresses to the digestible protein and fat.
gizzard. Protein provides 4 calories of energy for every gram of protein consumed, and is the same
amount derived from carbohydrates; fats deliver 9 calories per gram. Extra calories consumed are
stored as fat because it's such a concentrated source of energy. When a body requires energy, it first
Gizzard: The hind
part of the uses glucose from carbohydrates, then fatty acids. As long as enough calories are consumed from
stomach, other sources, protein is not turned into energy.
especially modified
for grinding food.
The gizzard has a
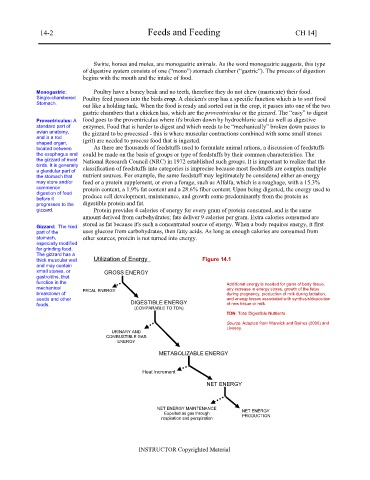
thick muscular wall Utilization of Energy Figure 14.1
and may contain
small stones, or GROSS ENERGY
gastroliths, that
function in the Additional energy is needed for gains of body tissue,
mechanical FECAL ENERGY any increase in energy stores, growth of the fetus
breakdown of during pregnancy, production of milk during lactation,
seeds and other and energy losses associated with synthesis/deposition
foods. DIGESTIBLE ENERGY of new tissue or milk.
(COMPARABLE TO TDN)
TDN: Total Digestible Nutrients
Source: Adapted from Warwick and Baines (2000) and
Livesey.
URINARY AND
COMBUSTIBLE GAS
ENERGY
METABOLIZABLE ENERGY
Heat Increment
NET ENERGY
NET ENERGY MAINTENANCE NET ENERGY
Expelled as gas through
respiration and perspiration PRODUCTION
INSTRUCTOR Copyrighted Material