Page 160 - Bus101FlipBook
P. 160
9-8 The Securities Market [CH 9
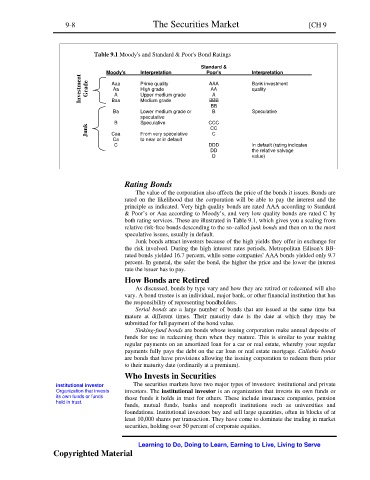
Table 9.1 Moody's and Standard & Poor's Bond Ratings
Standard &
Moody's Interpretation Poor's Interpretation
Investment Grade Aaa Prime quality AAA Bank investment
Aa
High grade
quality
AA
A
Upper medium grade
A
Baa
BBB
Medium grade
BB
Ba Lower medium grade or B Speculative
speculative
B Speculative CCC
Junk Caa From very speculative CC
C
Ca to near or in default
C DDD In default (rating indicates
DD the relative salvage
D value)
Rating Bonds
The value of the corporation also affects the price of the bonds it issues. Bonds are
rated on the likelihood that the corporation will be able to pay the interest and the
principle as indicated. Very high quality bonds are rated AAA according to Standard
& Poor’s or Aaa according to Moody’s, and very low quality bonds are rated C by
both rating services. These are illustrated in Table 9.1, which gives you a scaling from
relative risk-free bonds descending to the so‑called junk bonds and then on to the most
speculative issues, usually in default.
Junk bonds attract investors because of the high yields they offer in exchange for
the risk involved. During the high interest rates periods, Metropolitan Edison's BB-
rated bonds yielded 16.7 percent, while some companies' AAA bonds yielded only 9.7
percent. In general, the safer the bond, the higher the price and the lower the interest
rate the issuer has to pay.
How Bonds are Retired
As discussed, bonds by type vary and how they are retired or redeemed will also
vary. A bond trustee is an individual, major bank, or other financial institution that has
the responsibility of representing bondholders.
Serial bonds are a large number of bonds that are issued at the same time but
mature at different times. Their maturity date is the date at which they may be
submitted for full payment of the bond value.
Sinking-fund bonds are bonds whose issuing corporation make annual deposits of
funds for use in redeeming them when they mature. This is similar to your making
regular payments on an amortized loan for a car or real estate, whereby your regular
payments fully pays the debt on the car loan or real estate mortgage. Callable bonds
are bonds that have provisions allowing the issuing corporation to redeem them prior
to their maturity date (ordinarily at a premium).
Who Invests in Securities
institutional investor The securities markets have two major types of investors: institutional and private
Organization that invests investors. The institutional investor is an organization that invests its own funds or
its own funds or funds those funds it holds in trust for others. These include insurance companies, pension
held in trust. funds, mutual funds, banks and nonprofit institutions such as universities and
foundations. Institutional investors buy and sell large quantities, often in blocks of at
least 10,000 shares per transaction. They have come to dominate the trading in market
securities, holding over 50 percent of corporate equities.
Learning to Do, Doing to Learn, Earning to Live, Living to Serve
Copyrighted Material