Page 158 - Bus101FlipBook
P. 158
9-6 The Securities Market [CH 9
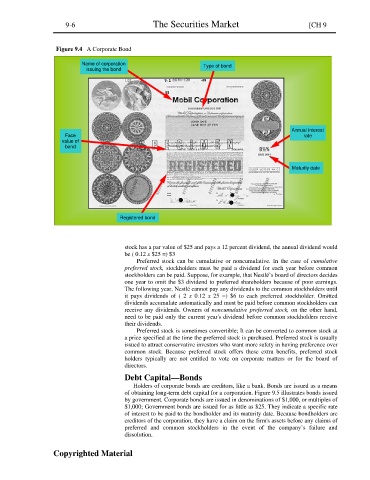
Figure 9.4 A Corporate Bond
Name of corporation
issuing the bond Type of bond
Annual interest
Face rate
value of
bond
Maturity date
Registered bond
stock has a par value of $25 and pays a 12 percent dividend, the annual dividend would
be ( 0.12 x $25 =) $3
Preferred stock can be cumulative or noncumulative. In the case of cumulative
preferred stock, stockholders must be paid a dividend for each year before common
stockholders can be paid. Suppose, for example, that Nestlé’s board of directors decides
one year to omit the $3 dividend to preferred shareholders because of poor earnings.
The following year, Nestlé cannot pay any dividends to the common stockholders until
it pays dividends of ( 2 x 0.12 x 25 =) $6 to each preferred stockholder. Omitted
dividends accumulate automatically and must be paid before common stockholders can
receive any dividends. Owners of noncumulative preferred stock, on the other hand,
need to be paid only the current year's dividend before common stockholders receive
their dividends.
Preferred stock is sometimes convertible; It can be converted to common stock at
a price specified at the time the preferred stock is purchased. Preferred stock is usually
issued to attract conservative investors who want more safety in having preference over
common stock. Because preferred stock offers these extra benefits, preferred stock
holders typically are not entitled to vote on corporate matters or for the board of
directors.
Debt Capital—Bonds
Holders of corporate bonds are creditors, like a bank. Bonds are issued as a means
of obtaining long-term debt capital for a corporation. Figure 9.5 illustrates bonds issued
by government. Corporate bonds are issued in denominations of $1,000, or multiples of
$1,000; Government bonds are issued for as little as $25. They indicate a specific rate
of interest to be paid to the bondholder and its maturity date. Because bondholders are
creditors of the corporation, they have a claim on the firm's assets before any claims of
preferred and common stockholders in the event of the company’s failure and
dissolution.
Copyrighted Material