Page 151 - Bus101FlipBook
P. 151
CH 8] Business 101 8-17
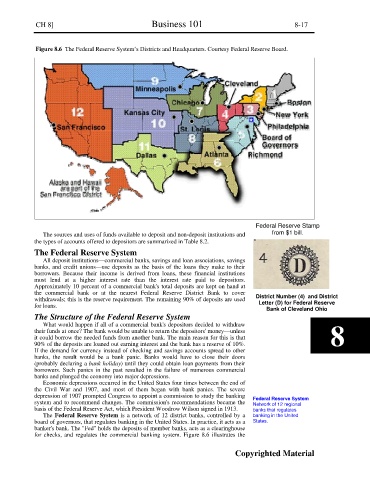
Figure 8.6 The Federal Reserve System’s Districts and Headquarters. Courtesy Federal Reserve Board.
Federal Reserve Stamp
The sources and uses of funds available to deposit and non-deposit institutions and from $1 bill.
the types of accounts offered to depositors are summarized in Table 8.2.
The Federal Reserve System
All deposit institutions—commercial banks, savings and loan associations, savings
banks, and credit unions—use deposits as the basis of the loans they make to their
borrowers. Because their income is derived from loans, these financial institutions
must lend at a higher interest rate than the interest rate paid to depositors.
Approximately 10 percent of a commercial bank's total deposits are kept on hand at
the commercial bank or at the nearest Federal Reserve District Bank to cover
withdrawals; this is the reserve requirement. The remaining 90% of deposits are used District Number (4) and District
for loans. Letter (D) for Federal Reserve
Bank of Cleveland Ohio
The Structure of the Federal Reserve System
What would happen if all of a commercial bank's depositors decided to withdraw
their funds at once? The bank would be unable to return the depositors' money—unless
it could borrow the needed funds from another bank. The main reason for this is that 8
90% of the deposits are loaned out earning interest and the bank has a reserve of 10%.
If the demand for currency instead of checking and savings accounts spread to other
banks, the result would be a bank panic. Banks would have to close their doors
(probably declaring a bank holiday) until they could obtain loan payments from their
borrowers. Such panics in the past resulted in the failure of numerous commercial
banks and plunged the economy into major depressions.
Economic depressions occurred in the United States four times between the end of
the Civil War and 1907, and most of them began with bank panics. The severe
depression of 1907 prompted Congress to appoint a commission to study the banking
system and to recommend changes. The commission's recommendations became the Federal Reserve System
Network of 12 regional
basis of the Federal Reserve Act, which President Woodrow Wilson signed in 1913. banks that regulates
The Federal Reserve System is a network of 12 district banks, controlled by a banking in the United
board of governors, that regulates banking in the United States. In practice, it acts as a States.
banker's bank. The "Fed" holds the deposits of member banks, acts as a clearinghouse
for checks, and regulates the commercial banking system. Figure 8.6 illustrates the
Copyrighted Material