Page 52 - Account for Ag - 2019
P. 52
9-4 Accounting for Agriculture CH 9]
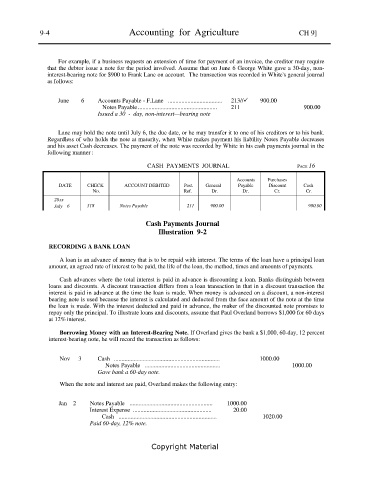
For example, if a business requests an extension of time for payment of an invoice, the creditor may require
that the debtor issue a note for the period involved. Assume that on June 6 George White gave a 30-day, non-
interest-bearing note for $900 to Frank Lane on account. The transaction was recorded in White's general journal
as follows:
June 6 Accounts Payable - F.Lane .................................... 213// 900.00
Notes Payable .................................................... 211 900.00
Issued a 30 - day, non-interest—bearing note
Lane may hold the note until July 6, the due date, or he may transfer it to one of his creditors or to his bank.
Regardless of who holds the note at maturity, when White makes payment his liability Notes Payable decreases
and his asset Cash decreases. The payment of the note was recorded by White in his cash payments journal in the
following manner :
CASH PAYMENTS JOURNAL PAGE 16
Accounts Purchases
DATE CHECK ACCOUNT DEBITED Post. General Payable Discount Cash
No. Ref. Dr. Dr. Cr. Cr.
20xx
July 6 318 Notes Payable 211 900.00 900.00
Cash Payments Journal
Illustration 9-2
RECORDING A BANK LOAN
A loan is an advance of money that is to be repaid with interest. The terms of the loan have a principal loan
amount, an agreed rate of interest to be paid, the life of the loan, the method, times and amounts of payments.
Cash advances where the total interest is paid in advance is discounting a loan. Banks distinguish between
loans and discounts. A discount transaction differs from a loan transaction in that in a discount transaction the
interest is paid in advance at the time the loan is made. When money is advanced on a discount, a non-interest
bearing note is used because the interest is calculated and deducted from the face amount of the note at the time
the loan is made. With the interest deducted and paid in advance, the maker of the discounted note promises to
repay only the principal. To illustrate loans and discounts, assume that Paul Overland borrows $1,000 for 60 days
at 12% interest.
Borrowing Money with an Interest-Bearing Note. If Overland gives the bank a $1,000, 60-day, 12 percent
interest-bearing note, he will record the transaction as follows:
Nov 3 Cash ...................................................................... 1000.00
Notes Payable .................................................. 1000.00
Gave bank a 60-day note.
When the note and interest are paid, Overland makes the following entry:
Jan 2 Notes Payable ....................................................... 1000.00
Interest Expense .................................................... 20.00
Cash ................................................................. 1020.00
Paid 60-day, 12% note.
Copyright Material