Page 22 - Bus101FlipBook
P. 22
1-10 Business and Economic Environments [CH 1
Economists measure
supply and demand in
relation to price and
quantity; then compare
them. Where supply
equals demand identifies
the equilibrium price and
quantity for a good or
service. This is an
historical equality that
changes as the
marketplace is a dynamic
(continually changing)
environment.
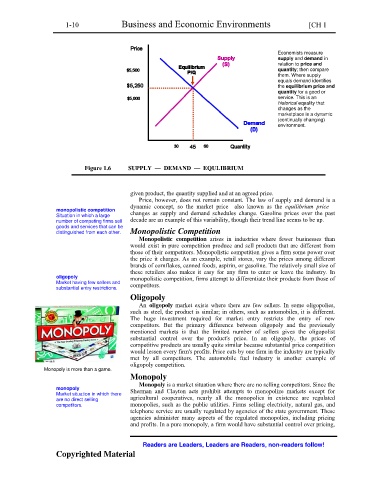
Figure 1.6 SUPPLY — DEMAND — EQULIBRIUM
given product, the quantity supplied and at an agreed price.
Price, however, does not remain constant. The law of supply and demand is a
dynamic concept, so the market price—also known as the equilibrium price—
monopolistic competition changes as supply and demand schedules change. Gasoline prices over the past
Situation in which a large
number of competing firms sell decade are an example of this variability, though their trend line seems to be up.
goods and services that can be
distinguished from each other. Monopolistic Competition
Monopolistic competition arises in industries where fewer businesses than
would exist in pure competition produce and sell products that are different from
those of their competitors. Monopolistic competition gives a firm some power over
the price it charges. As an example, retail stores, vary the prices among different
brands of cornflakes, canned foods, aspirin, or gasoline. The relatively small size of
these retailers also makes it easy for any firm to enter or leave the industry. In
oligopoly monopolistic competition, firms attempt to differentiate their products from those of
Market having few sellers and competitors.
substantial entry restrictions.
Oligopoly
An oligopoly market exists where there are few sellers. In some oligopolies,
such as steel, the product is similar; in others, such as automobiles, it is different.
The huge investment required for market entry restricts the entry of new
competitors. But the primary difference between oligopoly and the previously
mentioned markets is that the limited number of sellers gives the oligopolist
substantial control over the product's price. In an oligopoly, the prices of
competitive products are usually quite similar because substantial price competition
would lessen every firm's profits. Price cuts by one firm in the industry are typically
met by all competitors. The automobile fuel industry is another example of
oligopoly competition.
Monopoly is more than a game.
Monopoly
Monopoly is a market situation where there are no selling competitors. Since the
monopoly Sherman and Clayton acts prohibit attempts to monopolize markets except for
Market situation in which there
are no direct selling agricultural cooperatives, nearly all the monopolies in existence are regulated
competitors. monopolies, such as the public utilities. Firms selling electricity, natural gas, and
telephone service are usually regulated by agencies of the state government. These
agencies administer many aspects of the regulated monopolies, including pricing
and profits. In a pure monopoly, a firm would have substantial control over pricing,
Readers are Leaders, Leaders are Readers, non-readers follow!
Copyrighted Material