Page 142 - Bus101FlipBook
P. 142
8-8 Money, Banking & Financial Institutions [CH 8
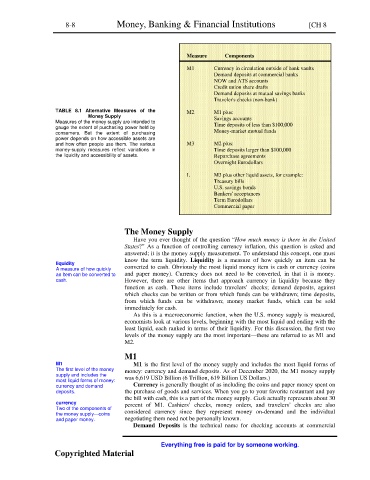
Measure Components
M1 Currency in circulation outside of bank vaults
Demand deposits at commercial banks
NOW and ATS accounts
Credit union share drafts
Demand deposits at mutual savings banks
Traveler's checks (non-bank)
TABLE 8.1 Alternative Measures of the M2 M1 plus:
Money Supply Savings accounts
Measures of the money supply are intended to
gauge the extent of purchasing power held by Time deposits of less than $100,000
consumers. But the extent of purchasing Money-market mutual funds
power depends on how accessible assets are
and how often people use them. The various M3 M2 plus:
money-supply measures reflect variations in Time deposits larger than $100,000
the liquidity and accessibility of assets. Repurchase agreements
Overnight Eurodollars
L M3 plus other liquid assets, for example:
Treasury bills
U.S. savings bonds
Bankers' acceptances
Term Eurodollars
Commercial paper
The Money Supply
Have you ever thought of the question “How much money is there in the United
States?” As a function of controlling currency inflation, this question is asked and
answered; it is the money supply measurement. To understand this concept, one must
know the term liquidity. Liquidity is a measure of how quickly an item can be
liquidity
A measure of how quickly converted to cash. Obviously the most liquid money item is cash or currency (coins
an item can be converted to and paper money). Currency does not need to be converted, in that it is money.
cash. However, there are other items that approach currency in liquidity because they
function as cash. These items include travelers’ checks; demand deposits, against
which checks can be written or from which funds can be withdrawn; time deposits,
from which funds can be withdrawn; money market funds, which can be sold
immediately for cash.
As this is a macroeconomic function, when the U.S. money supply is measured,
economists look at various levels, beginning with the most liquid and ending with the
least liquid, each ranked in terms of their liquidity. For this discussion, the first two
levels of the money supply are the most important—these are referred to as M1 and
M2.
M1
M1 M1 is the first level of the money supply and includes the most liquid forms of
The first level of the money money: currency and demand deposits. As of December 2020, the M1 money supply
supply and includes the was 6,619 USD Billion (6 Trillion, 619 Billion US Dollars.)
most liquid forms of money:
currency and demand Currency is generally thought of as including the coins and paper money spent on
deposits. the purchase of goods and services. When you go to your favorite restaurant and pay
the bill with cash, this is a part of the money supply. Cash actually represents about 30
currency percent of M1. Cashiers’ checks, money orders, and travelers’ checks are also
Two of the components of considered currency since they represent money on-demand and the individual
the money supply—coins
and paper money. negotiating them need not be personally known.
Demand Deposits is the technical name for checking accounts at commercial
Everything free is paid for by someone working.
Copyrighted Material