Page 54 - CalcBus_Flipbook
P. 54
6-4 Equations and Formulas CH 6]
depends on its age, this price is a dependent variable. Since the age of the vehicle does not depend on
the value of any other variable, the age is termed an independent variable.
Presume that the owner drives his vehicle at a rate of 30 miles per hour. Since the rate does not
change it is called a constant. A constant is a quantity that does not change in value. All arithmetic
numbers are constants. The distance the owner travels in any number of hours is d = rt or d = 30t.
Since the value of d depends on the value of t, when r is constant (30 miles per hour), then d is the
dependent variable and t is the independent variable. Usually, the literal number which stands alone
on one side of an equation is the dependent variable. Consider the Area of a circle.
Variables
Exponent
2
Area of a circle A = π r
Constant
———————— Rule to Remember —————————
A variable is a quantity whose value changes. A constant is a quantity whose value
never changes.
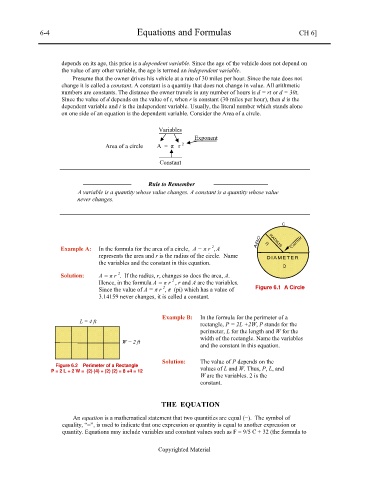
C
ARC RADIUS Center
2
Example A: In the formula for the area of a circle, A = π r , A R
represents the area and r is the radius of the circle. Name DIAMET ER
the variables and the constant in this equation.
D
2
Solution: A = π r . If the radius, r, changes so does the area, A.
2
Hence, in the formula A = π r , r and A are the variables.
2
Since the value of A = π r , π (pi) which has a value of Figure 6.1 A Circle
3.14159 never changes, it is called a constant.
L = 4 ft Example B: In the formula for the perimeter of a
rectangle, P = 2L +2W, P stands for the
perimeter, L for the length and W for the
width of the rectangle. Name the variables
W = 2 ft
and the constant in this equation.
Solution: The value of P depends on the
Figure 6.2 Perimeter of a Rectangle values of L and W. Thus, P, L, and
P = 2 L + 2 W = (2) (4) + (2) (2) = 8 +4 = 12
W are the variables. 2 is the
constant.
THE EQUATION
An equation is a mathematical statement that two quantities are equal (=). The symbol of
equality, “=”, is used to indicate that one expression or quantity is equal to another expression or
quantity. Equations may include variables and constant values such as F = 9/5 C + 32 (the formula to
Copyrighted Material