Page 178 - Calculating Agriculture Cover 20191124 STUDENT - A
P. 178
15-6 Metric Measurements CH 15]
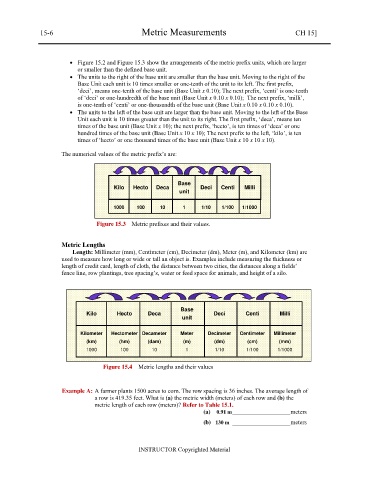
Figure 15.2 and Figure 15.3 show the arrangements of the metric prefix units, which are larger
or smaller than the defined base unit.
The units to the right of the base unit are smaller than the base unit. Moving to the right of the
Base Unit each unit is 10 times smaller or one-tenth of the unit to its left. The first prefix,
‘deci’, means one-tenth of the base unit (Base Unit x 0.10); The next prefix, ‘centi’ is one-tenth
of ‘deci’ or one-hundredth of the base unit (Base Unit x 0.10 x 0.10); The next prefix, ‘milli’,
is one-tenth of ‘centi’ or one-thousandth of the base unit (Base Unit x 0.10 x 0.10 x 0.10).
The units to the left of the base unit are larger than the base unit. Moving to the left of the Base
Unit each unit is 10 times greater than the unit to its right. The first prefix, ‘deca’, means ten
times of the base unit (Base Unit x 10); the next prefix, ‘hecto’, is ten times of ‘deca’ or one
hundred times of the base unit (Base Unit x 10 x 10); The next prefix to the left, ‘kilo’, is ten
times of ‘hecto’ or one thousand times of the base unit (Base Unit x 10 x 10 x 10).
The numerical values of the metric prefix’s are:
Base
Kilo Hecto Deca Deci Centi Milli
unit
1000 100 10 1 1/10 1/100 1/1000
Figure 15.3 Metric prefixes and their values.
Metric Lengths
Length: Millimeter (mm), Centimeter (cm), Decimeter (dm), Meter (m), and Kilometer (km) are
used to measure how long or wide or tall an object is. Examples include measuring the thickness or
length of credit card, length of cloth, the distance between two cities, the distances along a fields’
fence line, row plantings, tree spacing’s, water or feed space for animals, and height of a silo.
Base
Kilo Hecto Deca Deci Centi Milli
unit
Kilometer Hectometer Decameter Meter Decimeter Centimeter Millimeter
(km) (hm) (dam) (m) (dm) (cm) (mm)
1000 100 10 1 1/10 1/100 1/1000
Figure 15.4 Metric lengths and their values
Example A: A farmer plants 1500 acres to corn. The row spacing is 36 inches. The average length of
a row is 419.35 feet. What is (a) the metric width (meters) of each row and (b) the
metric length of each row (meters)? Refer to Table 15.1.
(a) 0.91 m ___________________ meters
(b) 130 m ___________________ meters
INSTRUCTOR Copyrighted Material