Page 54 - Bus101FlipBook
P. 54
3-8 Forms of Business Ownership [CH 3
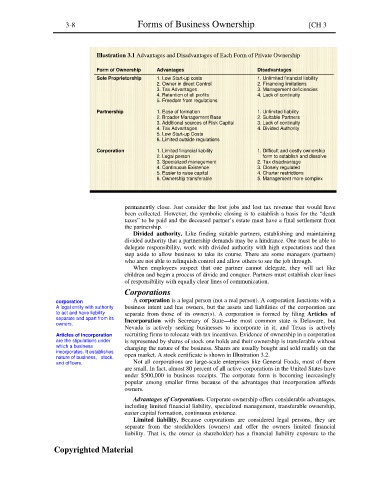
Illustration 3.1 Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Form of Private Ownership
Form of Ownership Advantages Disadvantages
Sole Proprietorship 1. Low Start-up costs 1. Unlimited financial liability
2. Owner in direct Control 2. Financing limitations
3. Tax Advantages 3. Management deficiencies
4. Retention of all profits 4. Lack of continuity
5. Freedom from regulations
Partnership 1. Ease of formation 1. Unlimited liability
2. Broader Management Base 2. Suitable Partners
3. Additional sources of Risk Capital 3. Lack of continuity
4. Tax Advantages 4. Divided Authority
5. Low Start-up Costs
6. Limited outside regulations
Corporation 1. Limited financial liability 1. Difficult and costly ownership
2. Legal person form to establish and dissolve
3. Specialized management 2. Tax disadvantage
4. Continuous Existence 3. Closely regulated
5. Easier to raise capital 4. Charter restrictions
6. Ownership transferable 5. Management more complex
permanently close. Just consider the lost jobs and lost tax revenue that would have
been collected. However, the symbolic closing is to establish a basis for the “death
taxes” to be paid and the deceased partner’s estate must have a final settlement from
the partnership.
Divided authority. Like finding suitable partners, establishing and maintaining
divided authority that a partnership demands may be a hindrance. One must be able to
delegate responsibility, work with divided authority with high expectations and then
step aside to allow business to take its course. There are some managers (partners)
who are not able to relinquish control and allow others to see the job through.
When employees suspect that one partner cannot delegate, they will act like
children and begin a process of divide and conquer. Partners must establish clear lines
of responsibility with equally clear lines of communication.
Corporations
corporation A corporation is a legal person (not a real person). A corporation functions with a
A legal entity with authority business intent and has owners, but the assets and liabilities of the corporation are
to act and have liability separate from those of its owner(s). A corporation is formed by filing Articles of
separate and apart from its Incorporation with Secretary of State—the most common state is Delaware, but
owners.
Nevada is actively seeking businesses to incorporate in it; and Texas is actively
Articles of incorporation recruiting firms to relocate with tax incentives. Evidence of ownership in a corporation
are the stipulations under is represented by shares of stock one holds and their ownership is transferable without
which a business changing the nature of the business. Shares are usually bought and sold readily on the
incorporates. It establishes open market. A stock certificate is shown in Illustration 3.2.
nature of business, stock,
and officers. Not all corporations are large-scale enterprises like General Foods, most of them
are small. In fact, almost 80 percent of all active corporations in the United States have
under $500,000 in business receipts. The corporate form is becoming increasingly
popular among smaller firms because of the advantages that incorporation affords
owners.
Advantages of Corporations. Corporate ownership offers considerable advantages,
including limited financial liability, specialized management, transferable ownership,
easier capital formation, continuous existence.
Limited liability. Because corporations are considered legal persons, they are
separate from the stockholders (owners) and offer the owners limited financial
liability. That is, the owner (a shareholder) has a financial liability exposure to the
Copyrighted Material