Page 65 - Account for Ag - 2019
P. 65
CH 10] Payroll Accounting & Payroll Taxes 10-7
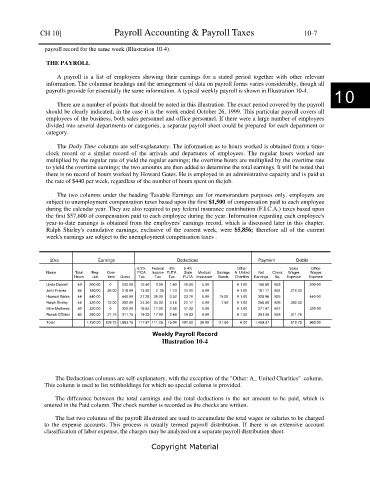
payroll record for the same week (Illustration 10-4).
THE PAYROLL
A payroll is a list of employees showing their earnings for a stated period together with other relevant
information. The columnar headings and the arrangement of data on payroll forms varies considerably, though all
payrolls provide for essentially the same information. A typical weekly payroll is shown in Illustration 10-4.
10
There are a number of points that should be noted in this illustration. The exact period covered by the payroll
should be clearly indicated; in the case it is the week ended October 26, 1999. This particular payroll covers all
employees of the business, both sales personnel and office personnel. If there were a large number of employees
divided into several departments or categories, a separate payroll sheet could be prepared for each department or
category.
The Daily Time columns are self-explanatory. The information as to hours worked is obtained from a time-
clock record or a similar record of the arrivals and departures of employees. The regular hours worked are
multiplied by the regular rate of yield the regular earnings; the overtime hours are multiplied by the overtime rate
to yield the overtime earnings; the two amounts are then added to determine the total earnings. It will be noted that
there is no record of hours worked by Howard Gates. He is employed in an administrative capacity and is paid at
the rate of $440 per week, regardless of the number of hours spent on the job.
The two columns under the heading Taxable Earnings are for memorandum purposes only. employers are
subject to unemployment compensation taxes based upon the first $1,500 of compensation paid to each employee
during the calendar year. They are also required to pay federal insurance contribution (F.I.C.A.) taxes based upon
the first $57,600 of compensation paid to each employee during the year. Information regarding each employee's
year-to-date earnings is obtained from the employees' earnings record, which is discussed later in this chapter.
Ralph Shirley's cumulative earnings, exclusive of the current week, were $5,856; therefore all of the current
week's earnings are subject to the unemployment compensation taxes .
20xx Earnings Deductions Payment Debits
6.2% Federal .8% 5.4% Other: Sales Office
Name Total Reg- Over- FICA Income FUTA State Medical Savings A United Net Check Wages Wages
Hours ular time Gross Tax Tax Tax FUTA Insurance Bonds Charities Earnings No. Expense Expense
Linda Darnell 40 200.00 0 200.00 12.40 3.00 1.60 10.80 6.00 A 1.00 166.80 923 200.00
John Franks 44 180/00 36.00 216.00 13.92 2. 25 1.73 11.66 6.00 A 1.00 181.17 924 216.00
Howard Gates 44 440.00 440.00 27.28 38.00 3.52 23.76 6.00 15.00 A 1.00 328.96 925 440.00
Ralph Shirley 46 320.00 72.00 392.00 24.30 34.00 3.14 21.17 6.00 7.50 A 1.00 258.88 926 392.00
Billie Mathews 40 320.00 0 320.00 19.84 17.00 2.56 17.28 6.00 A 1.00 271.97 927 320.00
Rosair O’Brian 42 290.00 21.75 311.75 19.33 17.00 2.49 16.83 6.00 A 1.00 251.59 928 311.75
Total 1,750.00 129.75 1,883.75 117.97 111.25 15.04 101.50 36.00 21.50 6.00 1,459.37 919.75 960.00
Weekly Payroll Record
Illustration 10-4
The Deductions columns are self-explanatory, with the exception of the "Other: A_ United Charities" column.
This column is used to list withholdings for which no special column is provided.
The difference between the total earnings and the total deductions is the net amount to be paid, which is
entered in the Paid column. The check number is recorded as the checks are written.
The last two columns of the payroll illustrated are used to accumulate the total wages or salaries to be charged
to the expense accounts. This process is usually termed payroll distribution. If there is an extensive account
classification of labor expense, the charges may be analyzed on a separate payroll distribution sheet.
Copyright Material