Page 105 - Calculating Agriculture Cover 20191124 STUDENT - A
P. 105
CH 9] Calculating Agriculture 9-17
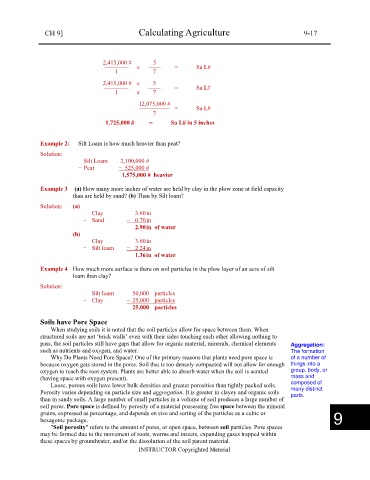
2,415,000 # 5
———— x —— = Sa L#
1 7
2,415,000 # x 5
———— —— = Sa L#
1 x 7
12,075,000 #
————— = Sa L#
7
1,725,000 # = Sa L# in 5 inches
Example 2: Silt Loam is how much heavier than peat?
Solution:
Silt Loam 2,100,000 #
− Peat − 525,000 #
1,575,000 # heavier
Example 3 (a) How many more inches of water are held by clay in the plow zone at field capacity
than are held by sand? (b) Than by Silt loam?
Solution: (a)
Clay 3.60 in
− Sand − 0.70 in
2.90 in of water
(b)
Clay 3.60 in
− Silt loam − 2.24 in
1.36 in of water
Example 4 How much more surface is there on soil particles in the plow layer of an acre of silt
loam than clay?
Solution:
Silt loam 50,000 particles
− Clay − 25,000 particles
25,000 particles
Soils have Pore Space
When studying soils it is noted that the soil particles allow for space between them. When
structured soils are not ‘brick walls’ even with their sides touching each other allowing nothing to
pass, the soil particles still have gaps that allow for organic material, minerals, chemical elements Aggregation:
such as nutrients and oxygen, and water. The formation
Why Do Plants Need Pore Space? One of the primary reasons that plants need pore space is of a number of
because oxygen gets stored in the pores. Soil that is too densely compacted will not allow for enough things into a
oxygen to reach the root system. Plants are better able to absorb water when the soil is aerated group, body, or
(having space with oxygen present). mass and
Loose, porous soils have lower bulk densities and greater porosities than tightly packed soils. composed of
Porosity varies depending on particle size and aggregation. It is greater in clayey and organic soils many distinct
parts.
than in sandy soils. A large number of small particles in a volume of soil produces a large number of
soil pores. Pore space is defined by porosity of a material possessing free space between the mineral
grains, expressed as percentage, and depends on size and sorting of the particles as a cubic or
hexagonic package. 9
"Soil porosity" refers to the amount of pores, or open space, between soil particles. Pore spaces
may be formed due to the movement of roots, worms and insects, expanding gases trapped within
these spaces by groundwater, and/or the dissolution of the soil parent material.
INSTRUCTOR Copyrighted Material