Page 198 - Bus101FlipBook
P. 198
21-10 International Trade [CH 21
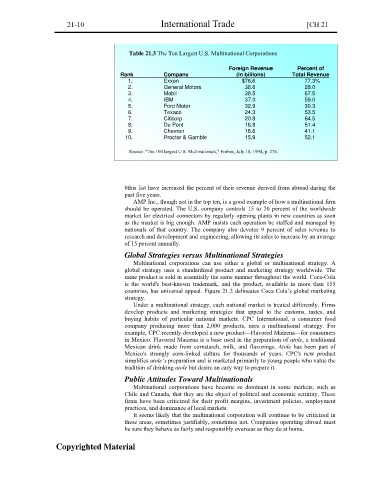
Table 21.3 The Ten Largest U.S. Multinational Corporations
Foreign Revenue Percent of
Rank Company (In bililons) Total Revenue
1. Exxon $76.6 77.3%
2. General Motors 38.6 28.0
3. Mobil 38.5 67.5
4. IBM 37.0 59.0
5. Ford Motor 32.9 30.3
6. Texaco 24.3 53.5
7. Citicorp 20.8 64.5
8. Du Pont 16.8 51.4
9. Chevron 16.6 41.1
10. Proctor & Gamble 15.9 52.1
Source: "The 100 largest U.S. Multinationals," Forbes, July 18, 1994, p. 276.
0this list have increased the percent of their revenue derived from abroad during the
past five years.
AMP Inc., though not in the top ten, is a good example of how a multinational firm
should be operated. The U.S. company controls 15 to 20 percent of the worldwide
market for electrical connectors by regularly opening plants in new countries as soon
as the market is big enough. AMP insists each operation be staffed and managed by
nationals of that country. The company also devotes 9 percent of sales revenue to
research and development and engineering, allowing its sales to increase by an average
of 15 percent annually.
Global Strategies versus Multinational Strategies
Multinational corporations can use either a global or multinational strategy. A
global strategy uses a standardized product and marketing strategy worldwide. The
same product is sold in essentially the same manner throughout the world. Coca-Cola
is the world's best-known trademark, and the product, available in more than 155
countries, has universal appeal. Figure 21.2 delineates Coca Cola’s global marketing
strategy.
Under a multinational strategy, each national market is treated differently. Firms
develop products and marketing strategies that appeal to the customs, tastes, and
buying habits of particular national markets. CPC International, a consumer food
company producing more than 2,000 products, uses a multinational strategy. For
example, CPC recently developed a new product—Flavored Maizena—for consumers
in Mexico. Flavored Maizena is a base used in the preparation of atole, a traditional
Mexican drink made from cornstarch, milk, and flavorings. Atole has been part of
Mexico's strongly corn-linked culture for thousands of years. CPC's new product
simplifies atole’s preparation and is marketed primarily to young people who value the
tradition of drinking atole but desire an easy way to prepare it.
Public Attitudes Toward Multinationals
Multinational corporations have become so dominant in some markets, such as
Chile and Canada, that they are the object of political and economic scrutiny. These
firms have been criticized for their profit margins, investment policies, employment
practices, and dominance of local markets.
It seems likely that the multinational corporation will continue to be criticized in
these areas, sometimes justifiably, sometimes not. Companies operating abroad must
be sure they behave as fairly and responsibly overseas as they do at home.
Copyrighted Material